India is doing remarkably well in the Ease of Doing Business Rankings which is published every year. Ranked 142 in the year 2014, India jumped to 100 last year, and according to the latest report published, India has now improved further and stands at rank 77.
Here are the salient points of the Ease of Doing Business, 2019 report with respect to India:
1. China and India—two of the world’s largest economies—are among the 10 top improvers with 13 reforms between the two nations.
2. The economies with the most notable improvement in Doing Business 2019 are Afghanistan, Djibouti, China, Azerbaijan, India, Togo, Kenya, Côte d’Ivoire, Turkey and Rwanda.
3. India now ranks 77 in the EODB rankings with a score of 67.23 with an improvement of 6.63 points in its score. India has improved 23 ranks in the last one year and 65 points in the last 4 years. India emerged as the BRICS and South Asian country to be recognised as the top improver in consecutive years. India has also ranked 1st among South Asian countries compared to 6th Rank in 2014.

4. The areas of improvement seem to be rather uniform in case of India.
5. According to the report, “India also focused on streamlining business processes. Under its National Trade Facilitation Action Plan 2017-2020, India implemented several initiatives that improved the efficiency of cross-border trade, reducing border and documentary compliance time for both exports and imports. Enhanced risk-based management now allows exporters to seal their containers electronically at their own facilities; as little as 5% of shipments must undergo physical inspections. India also invested in port equipment, strengthened management and improved electronic document flow. By implementing the Single Window Clearance System in Delhi and the Online Building Permit Approval System in Mumbai during the second half of 2017, India also continued to streamline and centralize its construction permitting process. Regarding getting electricity, newly-adopted regulations from the Delhi Electricity Regulatory Commission require that electrical connections be completed within 15 days of the application’s acceptance. To comply with this regulation, Tata Power Delhi Distribution deployed more personnel as well as tracking tools and key performance indicators to monitor each commercial connection”.
6. Although India jumped 30 ranks last year, as compared to 23 ranks this year, the Distance to Frontier score improvement shows that India has achieved more this year than last year. Last year, India’s score had improved by 4.71 points. This year, it has improved by 6.63 points. In fact, India is the 5th best-performing country based on DTF score improvement.
7. Djibouti and India are the only economies to make the list of 10 top improvers for the second consecutive year with India making 14 significant improvements in the same period.
8. India decreased border and documentary compliance time for both exports and imports.
9. In India the establishment of debt recovery tribunals reduced non- performing loans by 28% and lowered interest rates on larger loans, suggesting that faster processing of debt recovery cases cut the cost of credit.
9. The report mentions that research on electricity provision in India shows that the expansion of the electricity network boosts industrial development and increases the performance of smaller firms.
10. As one of the reforms, the report says that India (Mumbai) the Maharashtra Shops and Establishment Act, 2017, increased overtime hours and eliminated work restrictions on the weekly rest day while introducing a compensatory day off and a 100% wage premium for work on that day.
11. It also mentions how India has set a target of training 500 million people by 2022 to spur employment and national development.
12. The report says “India made starting a business easier by fully integrating multiple application forms into a general incorporation form. India also replaced the value-added tax with the GST (Goods and Services Tax) for which the registration process is faster. These reforms apply to both Delhi and Mumbai. At the same time, Mumbai abolished the practice of site inspections for registering companies under the Shops and Establishments Act”.
13. The report says that India has improved how it deals with construction permits. It says that India has streamlined the process of obtaining a building permit and made it faster and less expensive to obtain a construction permit. It also improved building quality control by introducing decennial liability and insurance. This reform applies to both Delhi and Mumbai.
14. The EODB has asserted that India strengthened access to credit by amending its insolvency law. Secured creditors are now given absolute priority over other claims within insolvency proceedings. This reform applies to both Delhi and Mumbai.
15. India has improved notably in 6 parameters. The improvements range from 132 ranks to 14 ranks in various parameters.
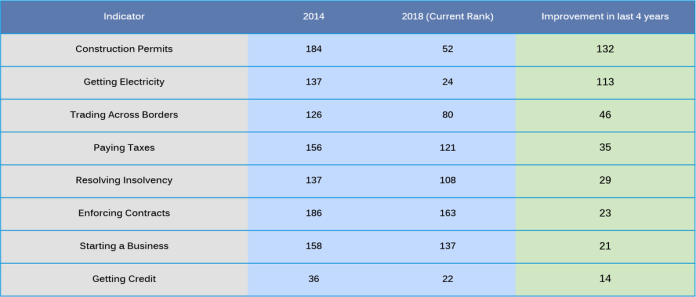
16. In all, India seems to be in an upword growth trajectory as far as business parameters are concerned. The sharp improvement is most evident from the graph tweeted by Minister Suresh Prabhu.






